[最も人気のある!] epimysium diagram 688265-Epimysium diagram
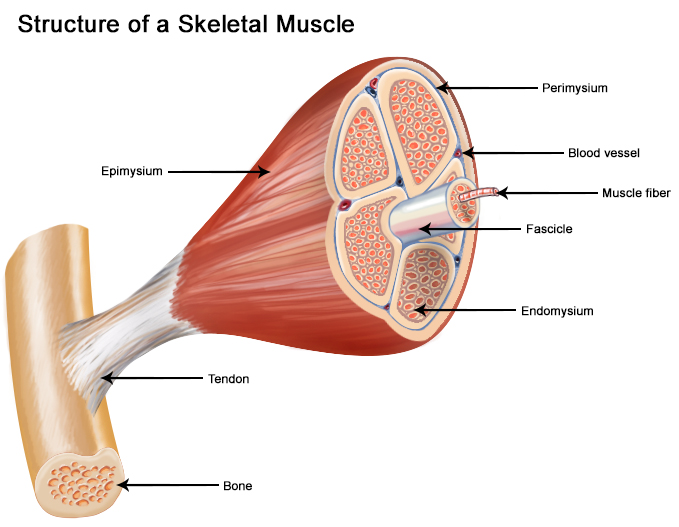
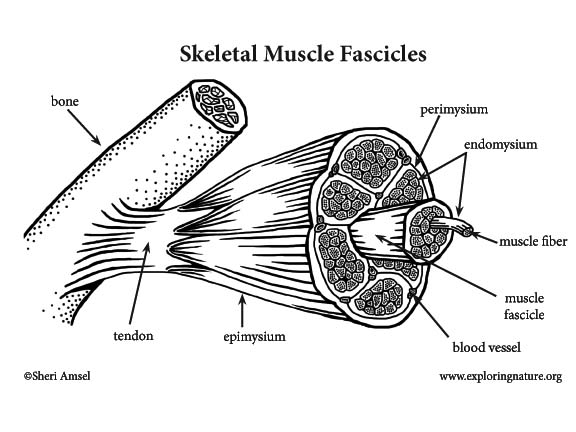
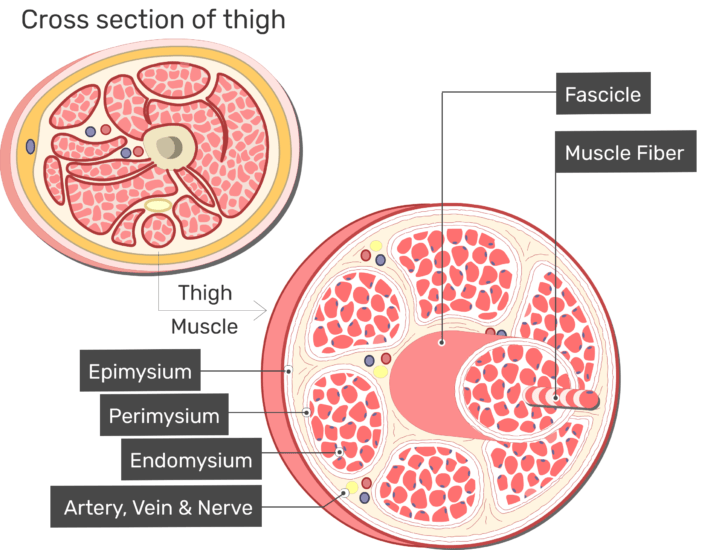
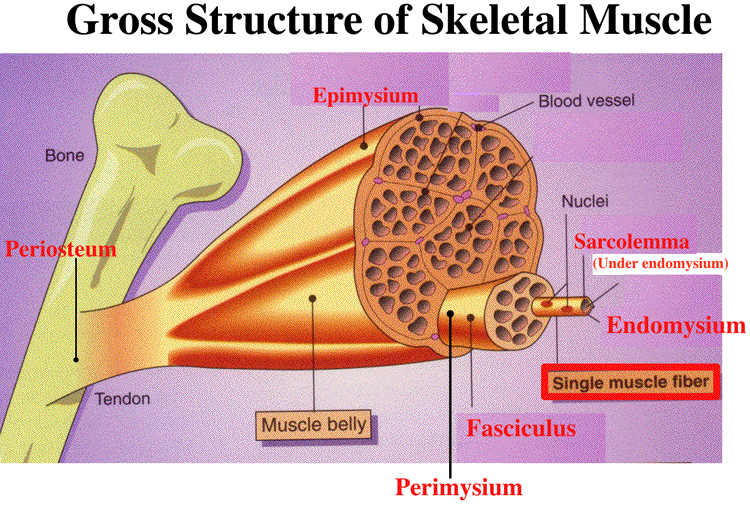
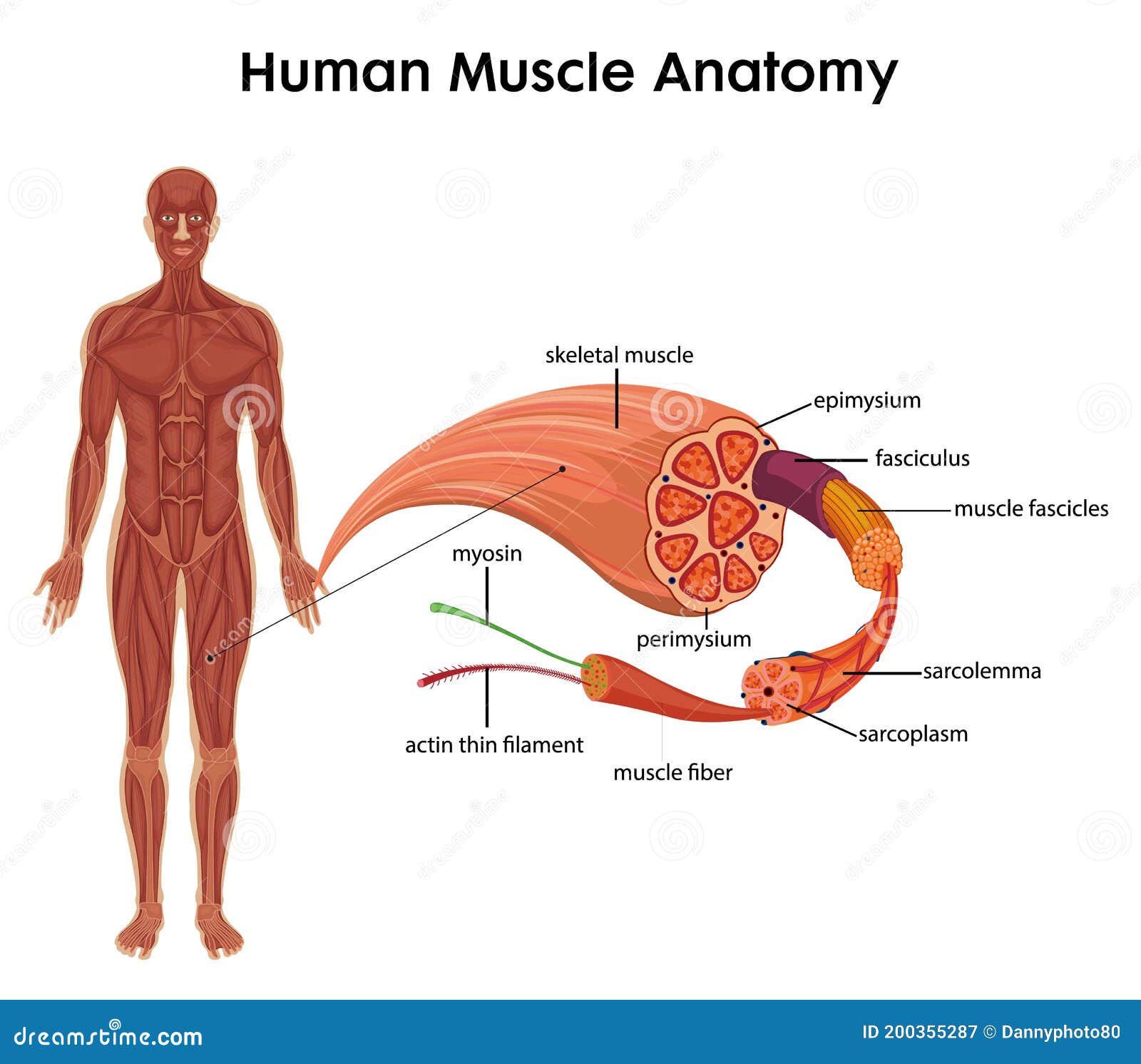
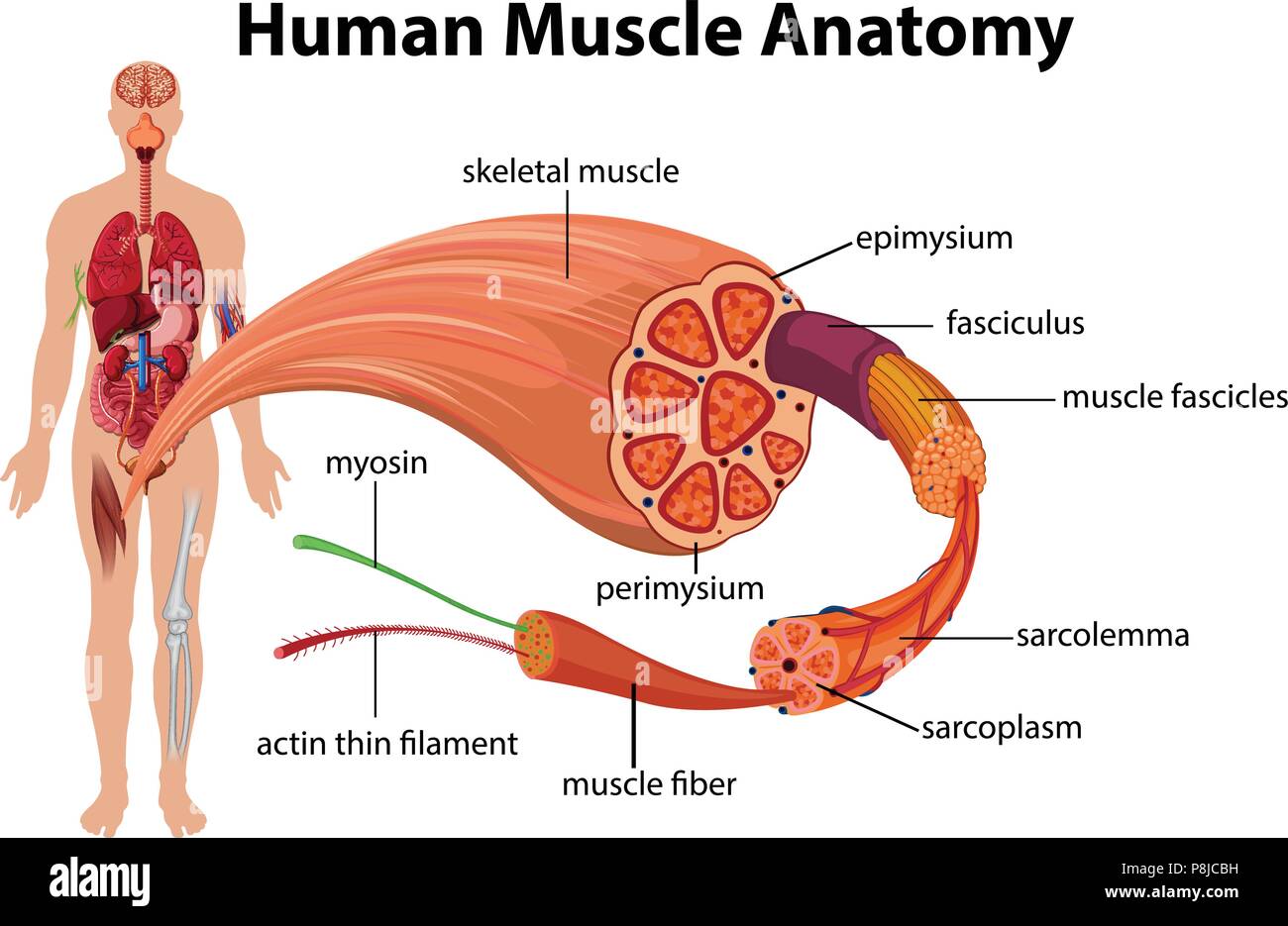
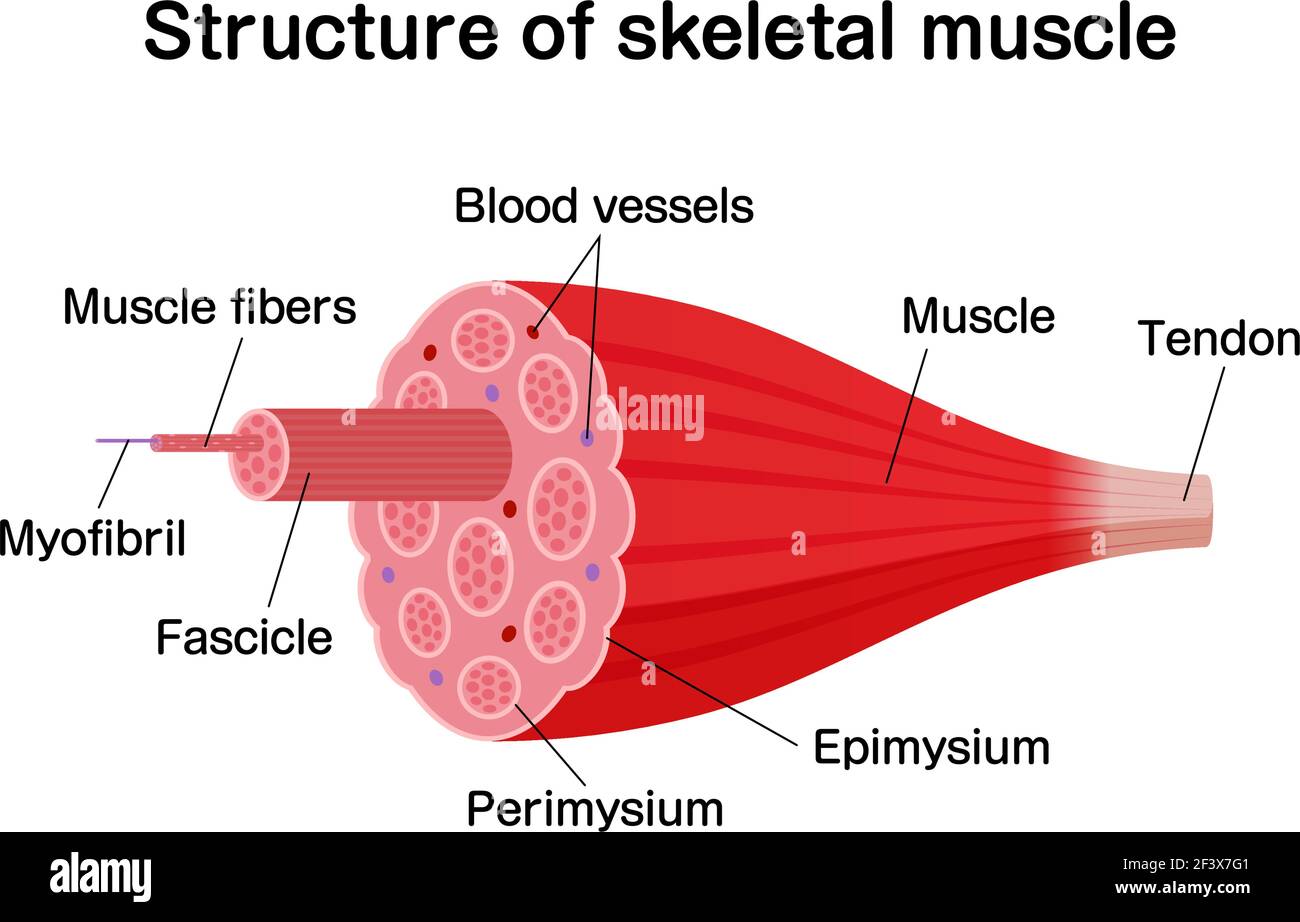
Musculoskeletal system The musculoskeletal system (locomotor system) is a human body system that provides our body with movement, stability, shape, and supportIt is subdivided into two broad systems Muscular system, which includes all types of muscles in the bodySkeletal muscles, in particular, are the ones that act on the body joints to produce movementsChapter 6 Connective tissue sheaths of skeletal muscle epimysium, perimysium, and endomysium Epimysium Bone Tendon Fascicle The external connectivetissue sheath of a muscle Dense, hard connective tissue composing the skeleton Strong connective tissue that attaches muscle to boneMuscle cells are also termed as muscle fibres They are long, cylindrical and multinucleated cells Muscle fibres were organized in three levels They are epimysium, endomysium and perimysium Muscles are covered by thick and tough connective tissues called as epimysium Epimysium separates one muscle from another

Cross Section Of Skeletal Muscle Diagram Png Image Transparent Png Free Download On Seekpng
Epimysium diagram
Epimysium diagram- Skeletal muscle tissue is made up of a collection of muscle fibers wrapped in connective tissue sheaths Endomysium, perimysium, epimysium muscle fibers are striated because of the arrangement of filaments in the Skeletal muscle micrograph shows a cross section of striated muscle demonstrating connective tissue and cell nucleiUse the following diagram for #22#26 to match the letter of the joint to its description a epimysium, endomysium, perimysium




Epimysium Images Stock Photos Vectors Shutterstock
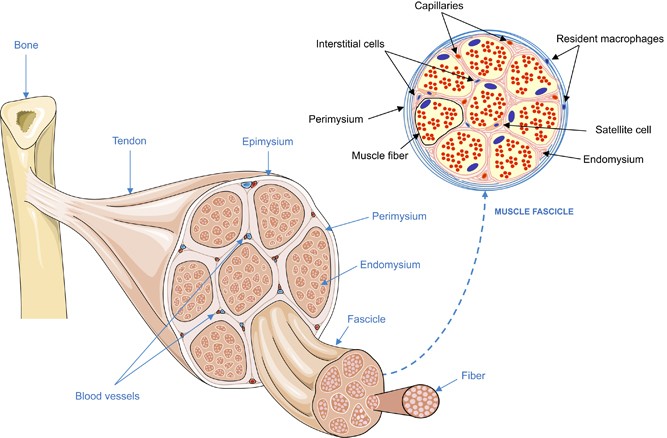
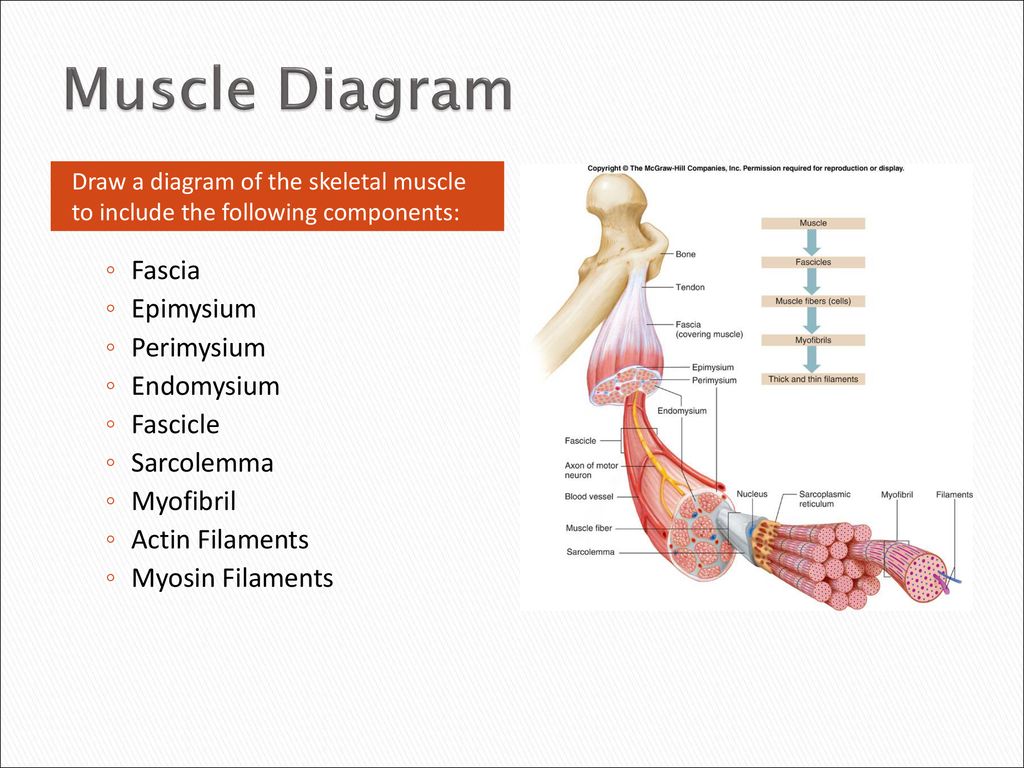
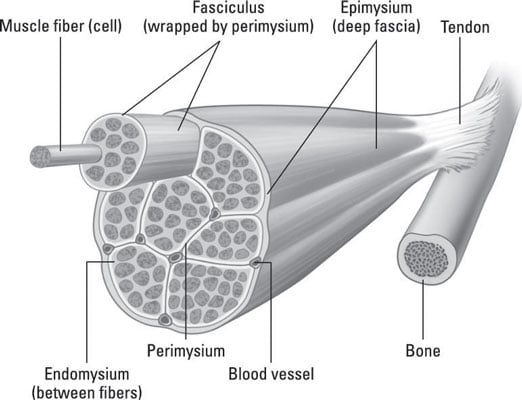
Epimysium = loose or dense connective tissue surrounding an entire muscle 2 perimysium = loose connective tissue defining muscle fascicles 3 endomysium = small amounts of loose ct surrounding individual muscle fibers Tendon protection A bursa = synovial pocket inserted between a tendon and a bony prominenceBeneath the epimysium each skeletal muscle consists of many muscle fibres arranged in bundles called fasciculi (sing, fasciculus or fascicle) Each bundle or fasciculus is surrounded by a connective tissue sheath, the perimysium and each muscle fibre or cell, is surrounded by a thin connective tissue sheath, the endomysiumMyo=muscle) ( #1 on the diagram)
Neuromuscular junction (Synapsis neuromuscularis) At its simplest, the neuromuscular junction is a type of synapse where neuronal signals from the brain or spinal cord interact with skeletal muscle fibers, causing them to contract The activation of many muscle fibers together causes muscles to contract, which in turn can produce movementEpimysium is a thick, elastic tissue made of collagen that surrounds whole muscles and prevents them from rubbing against other muscles or bones Finally, the epimysium is surrounded by fascia—a loose connective tissue that surrounds and supports organs in the bodyThe whole muscle is wrapped in a special type of connective tissue, epimysium Smooth muscle The smooth muscle is a type of nonstriated muscle, found within the tunica media layer of arteries and veins, the bladder, uterus, male and female reproductive tracts, gastrointestinal tract, respiratory tract, the ciliary muscle and iris of the eye
The epimysium also separates muscle from other tissues and organs in the area, allowing the muscle to move independently Figure 103 The Three Connective Tissue Layers Bundles of muscle fibers, called fascicles, are covered by the perimysium Muscle fibers areStructure of skeletal muscle explained Muscles fibres, actin, and myosin For more information and help learning muscle structure and composition visit htAntagonistic muscles labelled colouring sheet Body system outline coloring pages coloring pages for all ages User unfriendly and with no text to help with the diagrams This post is part of the free human body systems worksheets series




Epimysium Images Stock Photos Vectors Shutterstock



Muscle Fibers Epimysium Endomysium Perimysium Facicle
Skeletal Muscle Tissue Skeletal muscles most commonly attach to bones, and they help you move your body Unlike the other two types of muscle tissue, skeletal muscles contract on a voluntary basis via the somatic nervous system, allowing you to move your body at will Skeletal muscles also serve important functions, such as supporting your posture, protecting delicate organs, and theyMuscle enveloped by a membrane, the epimysium Now label the diagram in your workbook! Diagram of the muscletendonbone unit Skeletal muscle forming its fibrous framework The collagenous epimysium covering the muscle is well visualized as a silvery band on the surface of the posterior deltoid muscle (arrowheads) (Courtesy of Donald Resnick, MD, University of California, San Diego,




Epimysium Canvas Prints Fine Art America



2
Contains even larger blood vessels and nerves Three layers can be seen in slide 0593 View Image see orientationFigure 91 Connective tissue sheaths of skeletal muscle epimysium, perimysium, and endomysium Bone Perimysium Endomysium (between individual muscle fibers) Muscle fiber Fascicle (wrapped by perimysium) Epimysium Tendon Diagram of part of a muscle fiber showing the myofibrils One myofibril is extended afrom the cut end of the fiberA Connective tissue in the form of epimysium, perimysium, and endomysium surrounds the components of striated muscle as described above B Skeletal muscle is generally connected to bone via a piece of connective tissue called a tendon C



Skeletal Muscle Tissue



Seer Training Structure Of Skeletal Muscle
Nerve that penetrates the epimysium of a skeletal muscle The Nervous System It is the major controlling, regulatory, and communicating system in the body It is the center of all mental activity including thought, learning, and memory Together with the endocrine system (producing hormones), the nervous system is responsible for regulating and The muscles a back view Muscular system and the nervous system work together Pictures Skeletal System Worksheet Answers Signaturebymm Skeletal System Worksheet Skeletal System Worksheets Observe under the microscope in all 3 powers Muscular system worksheet pdf Note that the connective tissue coverings the epimysium perimy sium and endomysium areEpimysium the dense irregular connective tissue sheath around the entire muscle = deep fascia in gross anatomy;



Cell Death Clearance And Immunity In The Skeletal Muscle Cell Death Differentiation



Muscle Anatomy A Closer Look At Skeletal Muscle
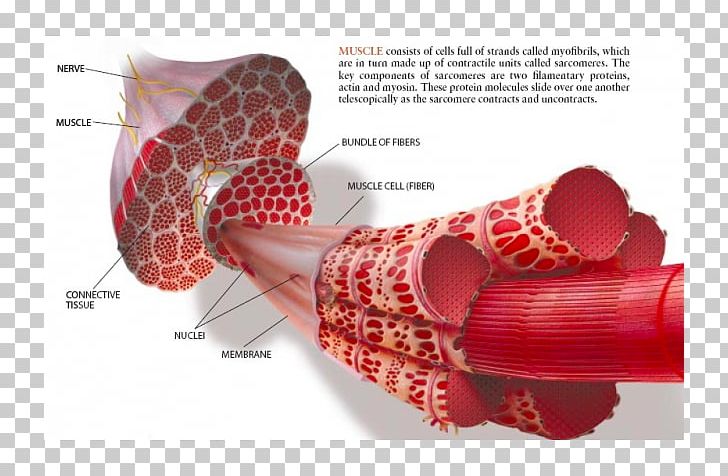
P, perimysium—the connective tissue layer surrounding the muscle bundles; Here you will easily identify the epimysium, perimysium and endomysium of skeletal muscle fibers You will also find the ovoid nuclei in the skeletal muscle fascicles at the periphery Muscle slide images and videos I think these labeled images and diagrams of skeletal muscle histology were helpful to understand the basics of this muscleMuscular tissue is a specialized tissue in animals which applies forces to different parts of the body by contraction It is made up of thin and elongated cells called muscle fibers It controls the movement of an organism The cytoplasm in the muscle fibers is called sarcoplasm It contains a network of membrane called the sarcoplasmic reticulum




Muscular System Latin Root Words Latin Root Word




Skeletal Muscle Structure Science Learning Hub
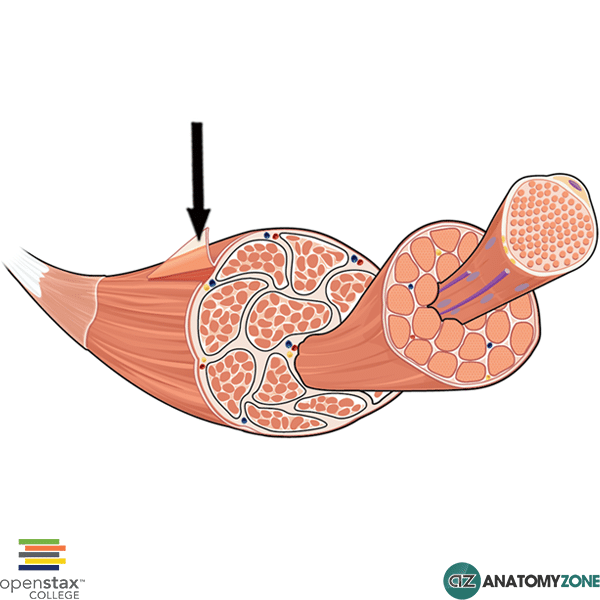
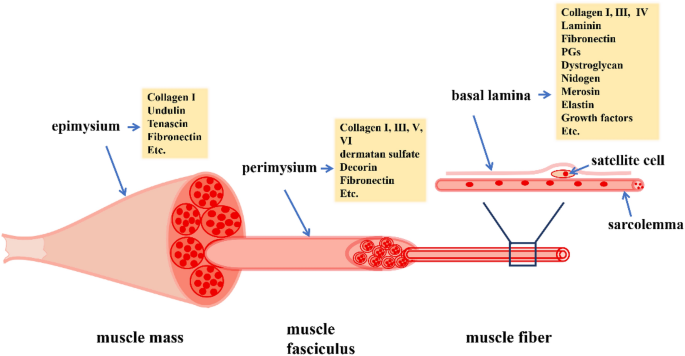
Answer (1 of 3) These are layers of connective tissue that surround individual muscle fibers (endomysium), bundles of muscle fibers called fascicles (perimysium) , and muscles (epimysium)Anatomy and Physiology questions and answers Muscle 1Epimysium F 2 Endomysium 1 Perimusium 1 Given the following diagram Label the indicated structures and Explain what this image represents with regard to form and function C Question Muscle 1Epimysium F 2 Endomysium 1 Perimusium 1 Given the following diagram Schematic diagram of the gross organization of muscle tissue and muscle ECMtendon organization (A) Muscle ECM can be categorized as epimysium (surrounding the muscle), perimysium (surrounding muscle fascicles), and endomysium (surrounding muscle fibers)




Muscle Anatomy Skeletal Muscle Structure Explained Teachpe Com




Jaypeedigital Ebook Reader
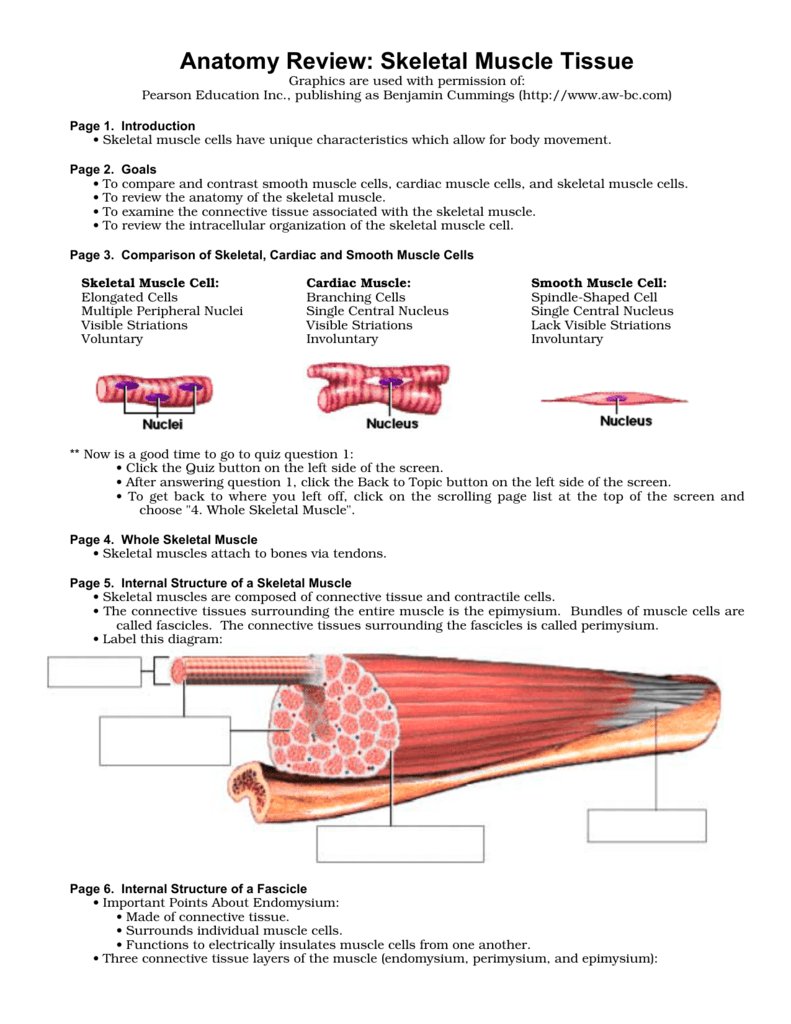
Under the deep fascia is the epimysium, occurring in the limbs and some regions of the trunk Skin ligaments connect the superficial fascia to the skin and to the deep fascia, forming a threedimensional network among the fat lobules The typical features of the superficial and deep fasciae and their relationships to nerves, vessels and musclesThe epimysium also separates muscle from other tissues and organs in the area, allowing the muscle to move independently Figure 1021 – The Three Connective Tissue Layers Bundles of muscle fibers, called fascicles, are covered by the perimysium Muscle• The connective tissues surrounding the entire muscle is the epimysium Bundles of muscle cells are called fascicles The connective tissues surrounding the fascicles is called perimysium • Label this diagram Page 6 Internal Structure of a Fascicle • Important Points About Endomysium • Made of connective tissue



Skeletal Muscle Muscle Contraction Epimysium Myofibril Png Clipart Actin Cell Endomysium Epimysium Miscellaneous Free Png Download




What Is The Structure Of Skeletal Muscle
Hand out the bottom diagram on page 14 or have students look at a diagram in the book as they find the following structures on their spaghetti model c The outer wrap of the spaghetti muscle is the CT that sits 'on top' of the muscle known as Epimysium (Epi=sit on top of;Figure 1 is a diagram of perimysium structure in different muscle types and Figure 2 shows light micrographs of endomysium and perimysium in bovine muscleRounding the muscle organ and outside the epimysium and tendon is called fascia Fascia is a general term for the fibrous connective tissue found under the skin and surrounding many deeper organs, including skeletal muscles and bones Fascia just under the skin (the hypodermis) is sometimes called superficial fascia,and the fascia around



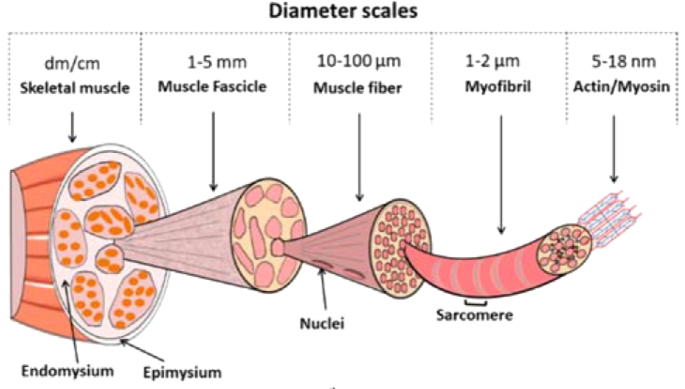
Skeletal Muscle Fiber Location And Arrangement




Muscle Architecture And Recruitment In Injury Rehab Nydnrehab Com
A, Note that the connective tissue coverings, the epimysium, perimysium, and endomysium, are continuous with each other and with the tendon Note also that muscle fibers are held together by the perimysium in groups called fascicles B, Diagram showing the arm in cross section Muscle Cell Diagram Types of Muscle Cell Muscle cells are commonly called Myocytes They are the specialized cells that makeup muscle tissue of the body Three connective tissue layers of the muscle are endomysium, perimysium, and epimysium They help to bind the muscle cells together, provide strength and support to the entire muscle The musculoskeletal system comprises one of the major tissue/organ systems in the body The three main types of muscle tissue are skeletal, cardiac, and smooth muscle groups123 Skeletal muscle attaches to the bone by tendons, and together they produce all the movements of the body The skeletal muscle fibers are crossed with a regular pattern of fine red




Epimysium An Overview Sciencedirect Topics




Nicmc Bmeg442 Engineering Exercise And Sports
Myosin and actin How tropomyosin and troponin regulate muscle contraction Role of the sarcoplasmic reticulum in muscle cells Anatomy of a skeletal muscle fiber This is the currently selected item Next lesson Immunology Sort byEp, epimysium—the connective tissue layer surrounding the entire muscle;The structure indicated in this diagram is the Epimysium Epimysium 7 Epimysium is a type of connective tissue that completely surrounds and encases muscles in humans and many animals It acts as a sort of buffer that protects muscles from rubbing into bones or other muscular fibers, and promotes smooth movement in the limbs and most joints



Muscle Diagram Fascia Epimysium Perimysium Endomysium Fascicle Ppt Download




The Fascia Connection The Mysiums Epimysium Which Means On Upon Or Above The Muscle Is The Fibrous Tissue Envelope That Surrounds Skeletal Muscle It Is A Layer Of Dense Irregular Connective
Diagram of cross section of skeletal muscle with epimysium and perimysium The diagram represents an axial cross section of a muscle belly, with two types of connective tissues shown The connective tissues include the outer sheath, epimysium, on the surface (thick circumferential circle) The perimysium (fine lines) includesEpimysium The epimysium (ep″ĭmis′eum;1 The layer of connective tissue that closely surrounds a skeletal muscle is called the _____ 2 Another layer of connective tissue, called the _____, extends inward from the epimysium and separates the muscle tissue into groups of muscle fibers



Gross Muscle And Sarcomere




The Structure And Role Of Intramuscular Connective Tissue In Muscle Function Abstract Europe Pmc
"outside the muscle") is an "overcoat" of dense irregular connective tissue that surrounds the whole muscle Sometimes it blends with the deep fascia that lies between neighboring muscles or the superficial fascia deep to the skin Perimysium and fascicles Within each skeletal muscle, the1 Label the diagram to the right with fascile, tendon, muscle fiber, endomysium, epimysium, perimysium, 2 Place the following words in order from largest to smallest fascicle, myofilament, myofibril, myofiber (muscle cell), sarcomere 3 List the 5 functions of the muscular system Bone Fascia MUSc(L I Axon of motor neuron X 4Use the following diagram for #22#26 to match the letter of the joint to its description a epimysium, endomysium, perimysium



What Is The Difference Between Epimysium And Fascia Pediaa Com




Zane Tippett Massage Breakdown Of Skeletal Muscles Muscle Components Several Sheaths Of Connective Tissue Hold The Fibers Of A Skeletal Muscle Together These Sheaths From External To Internal These Sheaths From
Epimysium 2 Color the perimysium around the extruded fascicle and in the cross section 3 Color the fascicle that is labeled in the cross section, and one additional fascicle 4 Color the endomysium around the extruded muscle fiber Outline some muscle fibers in the crosssection with the same color, because the endomysium surrounds all The free body diagram of the epimysium 'u_top' and 'u_bottom' are the displacements the underside of the upper collagen fiber and the topside of the lower collagen fiber along the direction, respectivelyWrapped in epimysium Î Epimysium and perimysium tissues taper at each end to form tendons Cartilage 3 types Î Hyaline cartilage z Solid matrix, cells (chrondrocytes) densely clustered z present in the growth plates at the end of bones and on the articular surfaces of joints Also present in the respiratory tract (eg trachea) Î Fibrocartilage




Epimysium Images Stock Photos Vectors Shutterstock




Muscle Contraction Sliding Filament Theory Teachpe Com
On the following figure, label a blood vessel, Question 180 Review Sheet 11 5 The diagram illustrates a small portion of several myofibrils Using letters from the key, correctly identify each structure indicated by a leader line or a bracket Key a A band d myosin filament g



What Are The Epimysium Perimysium And The Endomysium Quora



Epimysium Stock Illustrations 24 Epimysium Stock Illustrations Vectors Clipart Dreamstime




Effects Of External Stimulators On Engineered Skeletal Muscle Tissue Maturation Mueller 21 Advanced Materials Interfaces Wiley Online Library




Structure Of Muscle Anatomy Epimysium Covers Each Muscle Muscle Download Scientific Diagram
:background_color(FFFFFF):format(jpeg)/images/library/13584/skeletal-muscle-tissue_english.jpg)



Skeletal Muscle Tissue Histology Kenhub




2 Skeletal Muscle Structure The Entire Muscle Is Surrounded By The Download Scientific Diagram



Cardiac Muscle




Cross Section Of Skeletal Muscle Diagram Png Image Transparent Png Free Download On Seekpng




Epimysium Free Vector Eps Cdr Ai Svg Vector Illustration Graphic Art




Test 5 Skeletal Muscle Diagram Quiz Flashcards Quizlet




Muscle Fiber Diagram Quizlet




Figure Skeletal Muscles Sarcolemma Myofibril Motor Statpearls Ncbi Bookshelf




Level 3 41 Exercise And Fitness Knowledge Personal Trainer The Structure Of Skeletal Muscle Amac Training



2 The Layers Of The Deep Fascia From The Epimysium Of The Muscle To The Download Scientific Diagram




Skeletal Muscle Structure Illustration Puzzle For Sale By Spencer Sutton



Epimysium Anatomyzone



Epimysium High Resolution Stock Photography And Images Alamy




Human Muscle Epimysium Perimysium And Endomysium Youtube




L 4 Labelling Components Of Skeletal Muscle Diagram Quizlet



Extracellular Matrix An Important Regulator Of Cell Functions And Skeletal Muscle Development Cell Bioscience Full Text




Epimysium Clip Art Royalty Free Gograph




Skeletal Muscle Tissue Anatomy Pages The Connective Tissue Sheaths Of The Epimysium Perimysium And Endomysium Are Continuous With One Another Ppt Download




Epimysium An Overview Sciencedirect Topics



Skeletal Muscle High Resolution Stock Photography And Images Alamy




Stem Cells And Plasticity Of Skeletal Muscle Cell Differentiation Potential Application To Cell Therapy For Degenerative Muscular Diseases Regenerative Medicine




What S The Big Deal About Fascia Medical Massage Group




10 2 Skeletal Muscle Anatomy Physiology




Skeletal Muscle Physiology Content



Anatomy Review Skeletal Muscle Tissue




Medicine Hack Endomysium Perimysium And Epimysium Definition Histology



Pulling Together Muscles As Organs Dummies




Histology Of Muscle



Regenerative Medicine For Skeletal Muscle Loss A Review Of Current Tissue Engineering Approaches Springerlink



1




Style Medical 3 Molecular Cell 1 Piece Powerpoint Presentation Diagram Template Slide Powerpoint Templates Designs Ppt Slide Examples Presentation Outline




Epimysium Anatomy Definition Anatomy Drawing Diagram
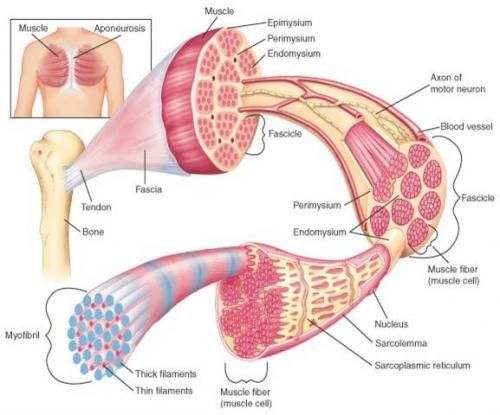



Skeletal Muscle Diagram



1
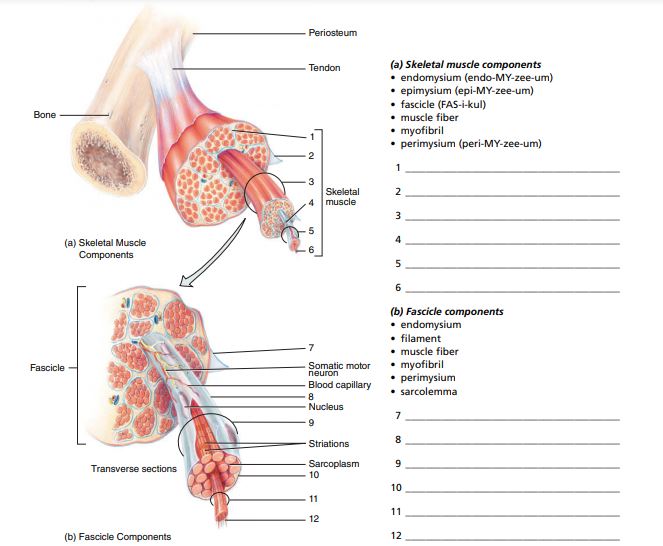



Answered Periosteum A Skeletal Muscle Bartleby
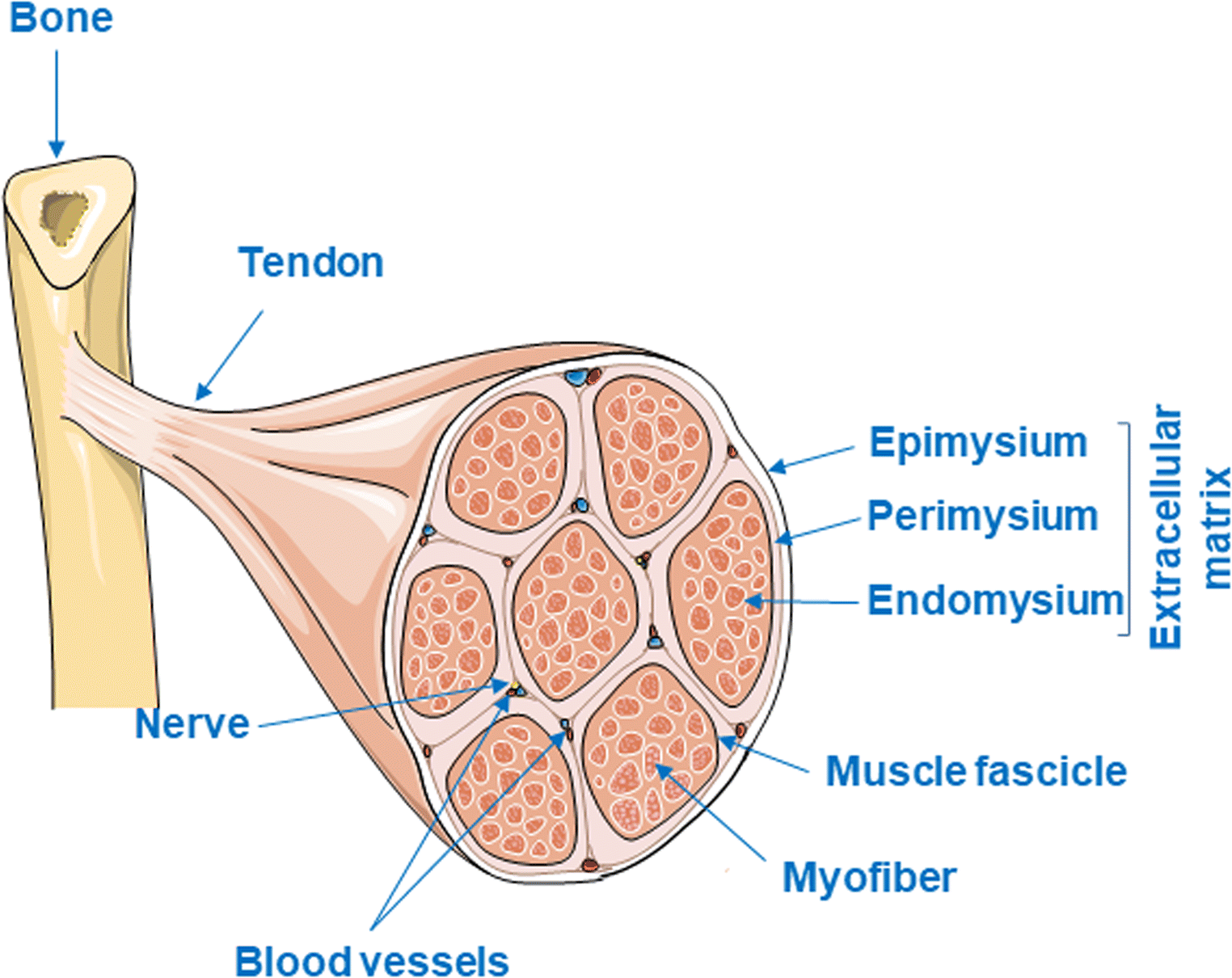



Figure 1 Skeletal Muscle Fibrosis An Overview Springerlink




Lab 7 Muscle Anatomy Review Flashcards Chegg Com
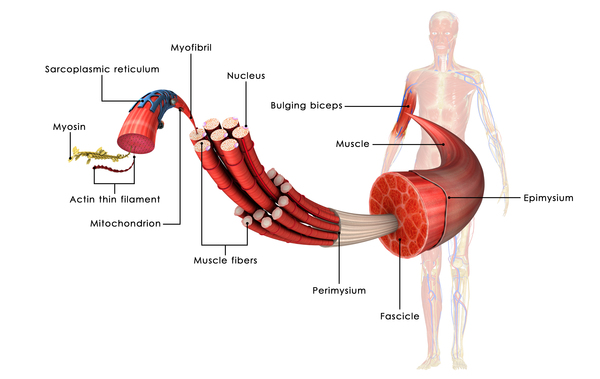



Myostatin Related Muscle Hypertrophy Medlineplus Genetics




Skeletal System 2 Structure And Function Of The Musculoskeletal System Nursing Times



2
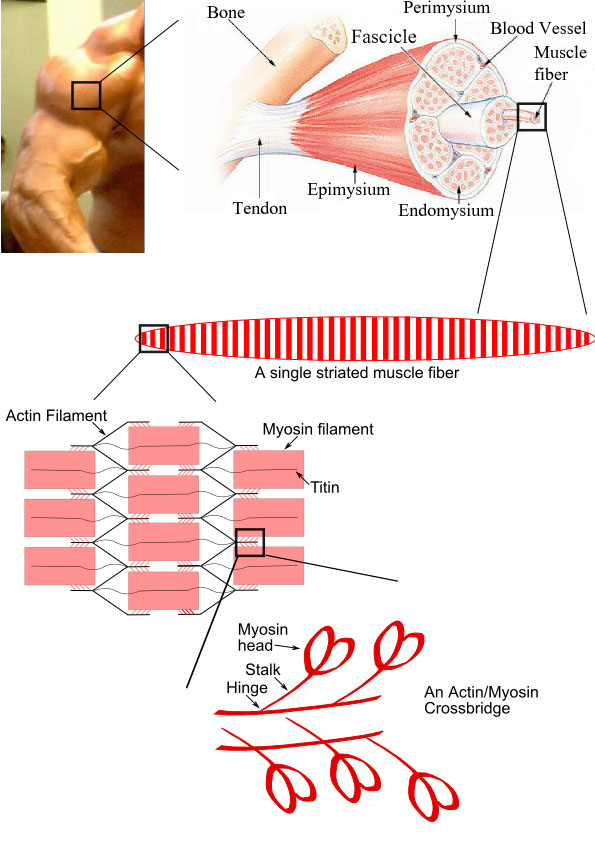



File Skeletal Muscle Diagram Jpg Wikimedia Commons




Gymnazio Health And Fitness Expert The Gross Structure Of Skeletal Muscle The Whole Muscle The Fasciculus And Individual Muscle Fibers Are Surrounded By The Connective Tissues Epimysium Perimysium And Endomysium Respectively




6 6 Muscle Structure And Function Support Systems In Animals Siyavula




File Tendon Anatomy Tendon Epimysium Fascicle Fiber Fibril Etc Smart Servier Cropped Jpg Wikimedia Commons
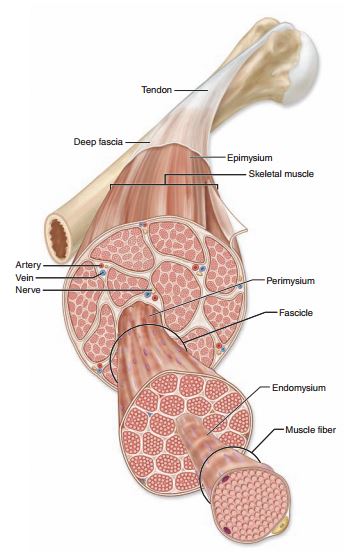



Fascial Layers Part 1 Anatomy Of A Muscle Tami Apland
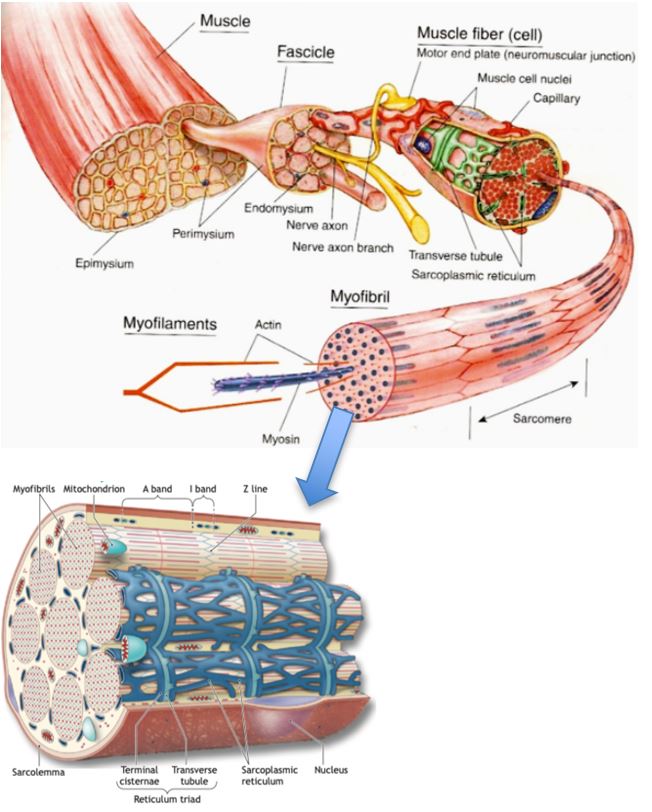



How Muscles Work Part 1 Of 2 Shapelog




2 Skeletal Muscle Structure Showing The 3 Types Of Connective Tissues Download Scientific Diagram




Skeletal Muscle Adaptations And Passive Muscle Stiffness In Cerebral Palsy A Literature Review And Conceptual Model In Journal Of Applied Biomechanics Volume 35 Issue 1




2 The Layers Of The Deep Fascia From The Epimysium Of The Muscle To The Download Scientific Diagram



Muscle Anatomy Structure Sport Fitness Advisor




2 Skeletal Muscle Structure The Entire Muscle Is Surrounded By The Download Scientific Diagram




What Is Epimysium Youtube



Untitled Document
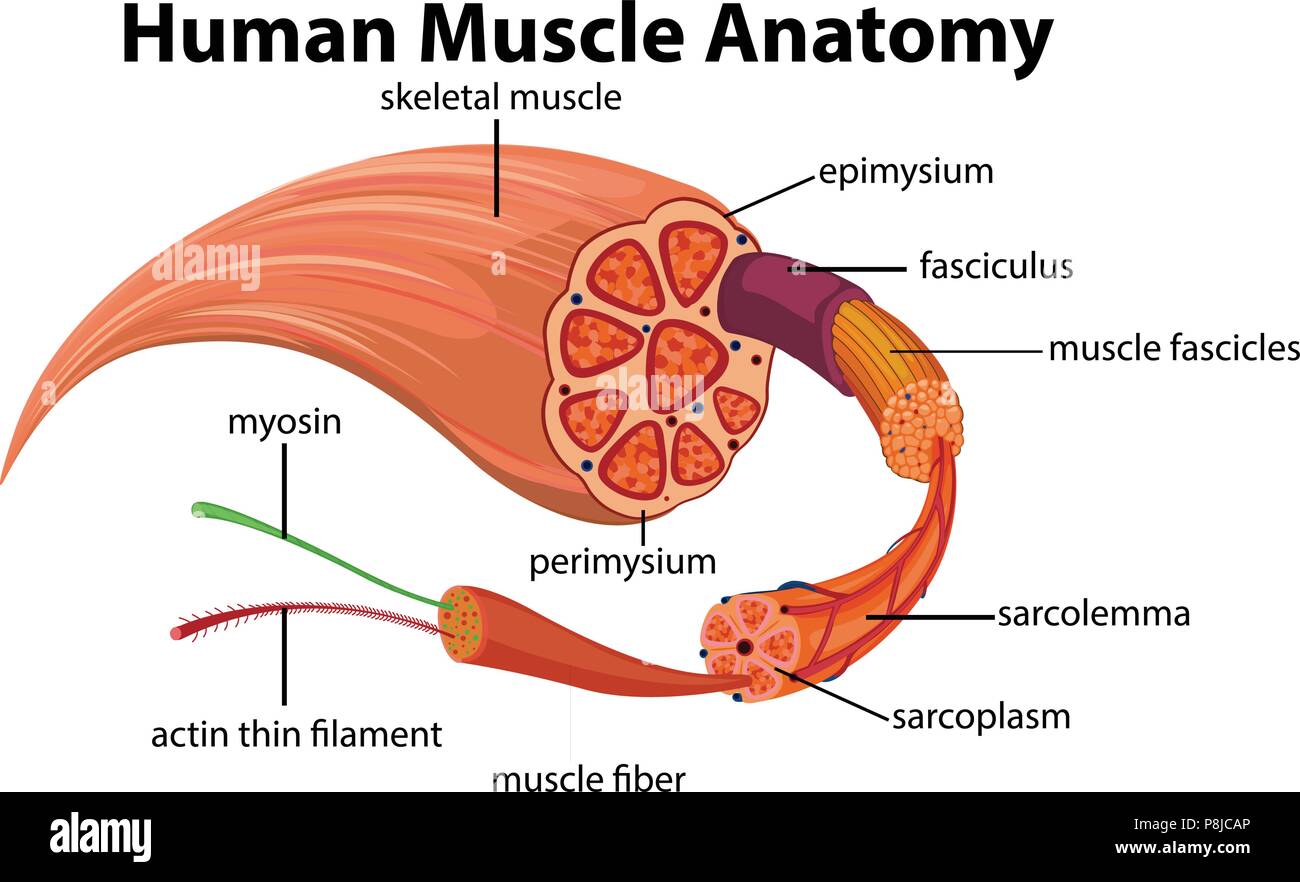



Human Muscle Anatomy Diagram Illustration Stock Vector Image Art Alamy




Complete Human Muscle Diagrams 19 101 Diagrams Muscle Diagram Muscular System Skeletal System Worksheet



What Is The Difference Between Epimysium And Fascia Quora




Epimysium An Overview Sciencedirect Topics
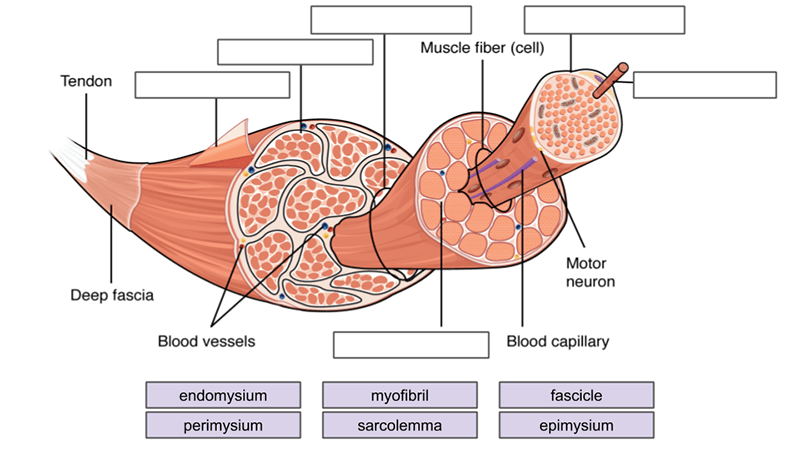



Muscles Labeling




Muscular System Freeze Dont Move A Muscle Can
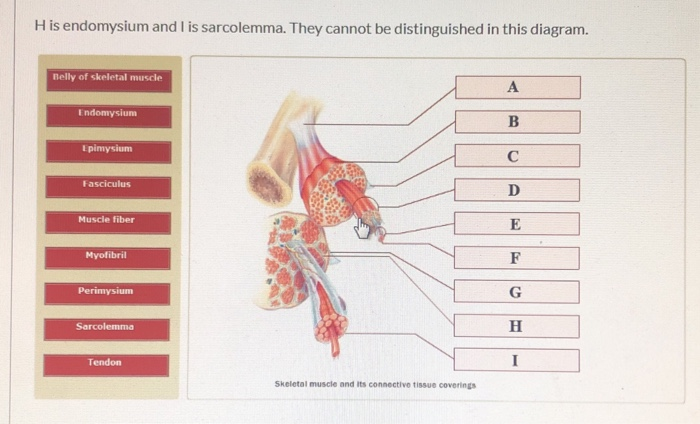



Solved H Is Endomysium And I Is Sarcolemma They Cannot Be Chegg Com




Anatomy Of Skeletal Muscle Diagram Quizlet




Connective Tissue Sheaths Of Skeletal Muscle Diagram Quizlet



Perimysium




Muscle Fascia And Force Transmission Journal Of Bodywork And Movement Therapies




Epimysium Stock Photos And Images Agefotostock




Epimysium Wikipedia




10 2 Skeletal Muscle Anatomy Physiology




Reading Php Lab




Skeletal Muscle Anatomy And Physiology
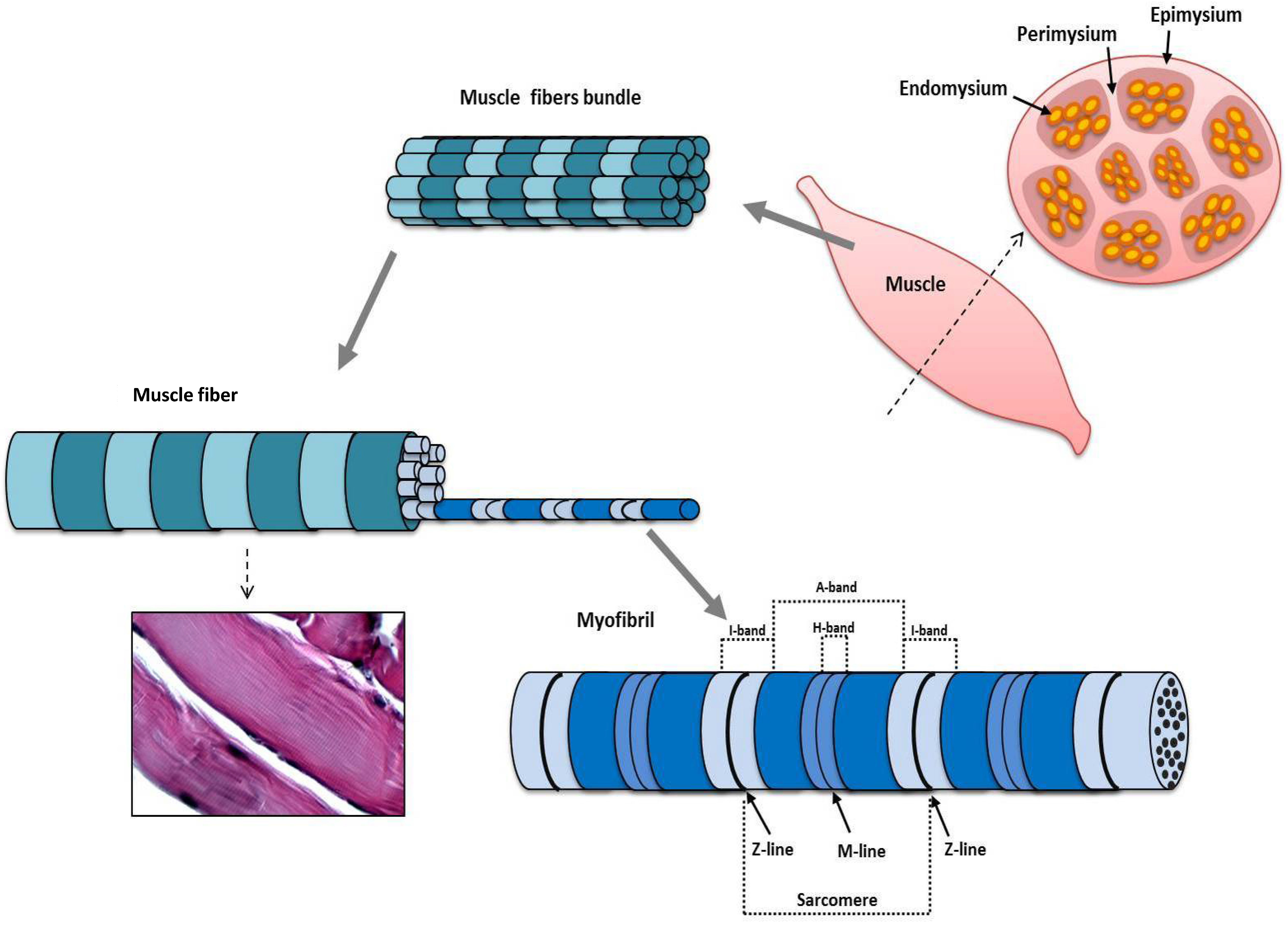



Jfmk Free Full Text Morphological And Functional Aspects Of Human Skeletal Muscle Html
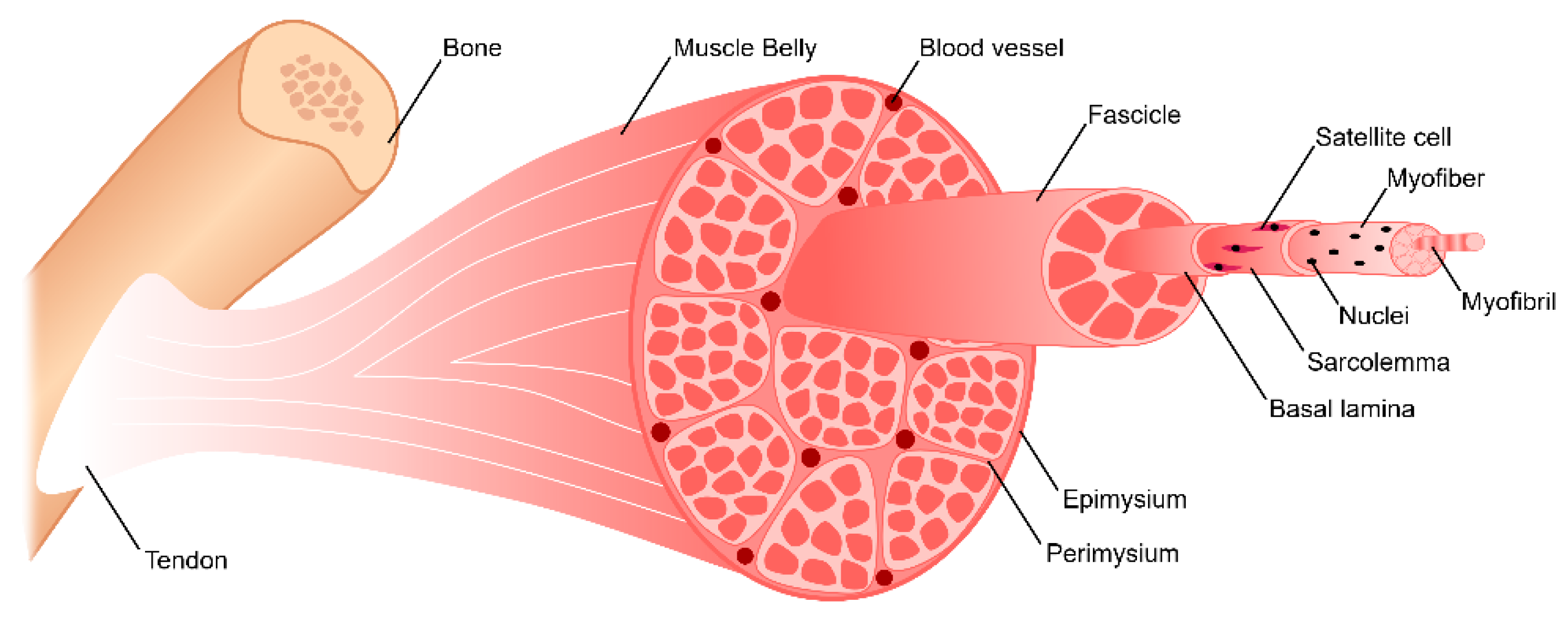



Bioengineering Free Full Text Skeletal Muscle Tissue Engineering Biomaterials Based Strategies For The Treatment Of Volumetric Muscle Loss Html



Skeletal Muscle Physiology




Skeletal Muscle Wikipedia




Epimysium Images Stock Photos Vectors Shutterstock
コメント
コメントを投稿